
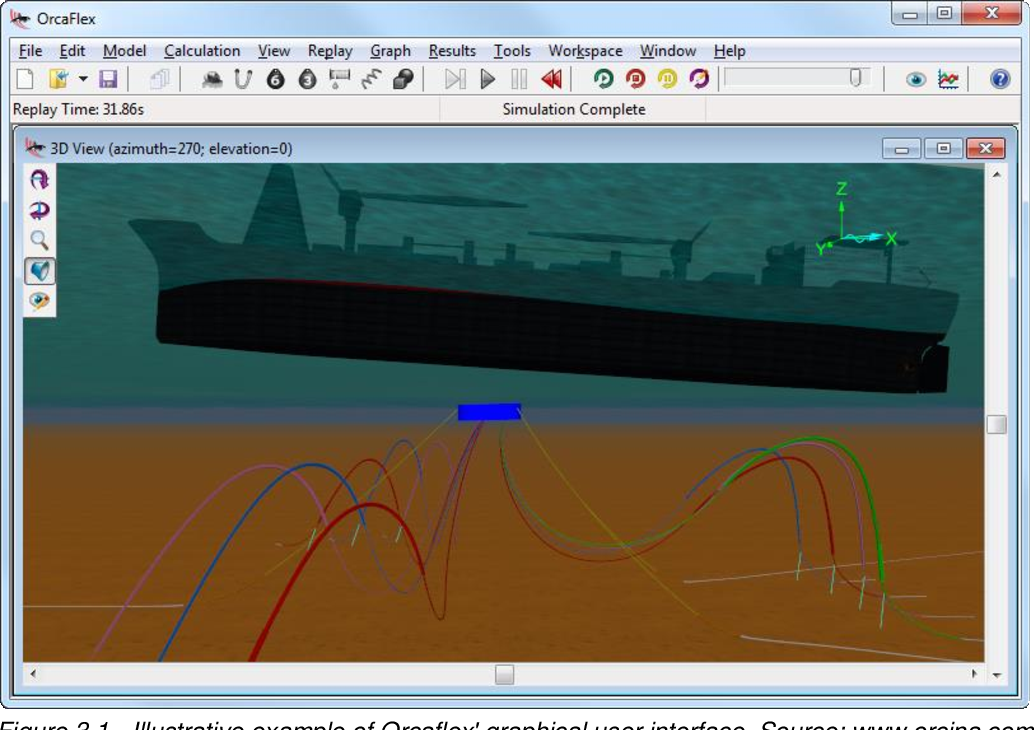
An overview of all available properties of the nodes is added. DAVE will automatically determine where the fluid is. Just add mesh as define how much fluid is inside it. They work in the same way as buoyancy meshes.
ORCAFLEX DEF DYNAMICSPROGRESS FREE
If the file is periodic, as recorded in the file header, OrcaFlex will interpret the data accordingly. Tanks with a free fluid surface are now available. bts file format supports periodic time histories. If you have the wind speed $v(h)$ at some other height h (in metres), then the wind speed $V(10)$ at 10m can be estimated using the formula $v(10) = v(h)\,(10/h)^$ respectively. If you are using the OCIMF model for wind load on vessels, the speed is expected to be that at an elevation of 10m (32.8 ft) above the mean water level (MWL). Negative factors may be used, allowing you to model reversing wind profiles.Ī value of '~' means that there is no vertical variation. To do so, you define a vertical variation factor variable data source. To specify a vertical wind speed profile, you may define the wind speed variation with height above the mean water level (MWL) as a dimensionless multiplicative factor.

Wind speed is assumed to be the same at all heights, unless a vertical wind speed profile is specified. The value here is fixed and cannot be edited. The air density is assumed to be constant and the same everywhere. You may choose whether or not wind loads are included for vessels, lines, 6D buoys and 6D buoy wings.


ORCAFLEX DEF DYNAMICSPROGRESS SOFTWARE
In order to minimise effort, Flexcom allows you to import RAO data directly from third-party software data files. from a radiation-diffraction program), and the conventions used are rarely consistent with the standard format expected by Flexcom itself. Quite often, RAO data is sourced externally (e.g. One area of particular importance is the definition of vessel RAO data. Flexcom, like most other programs, has its own set of conventions regarding the specification of input data.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
